1. Understanding Cataract Surgery
A
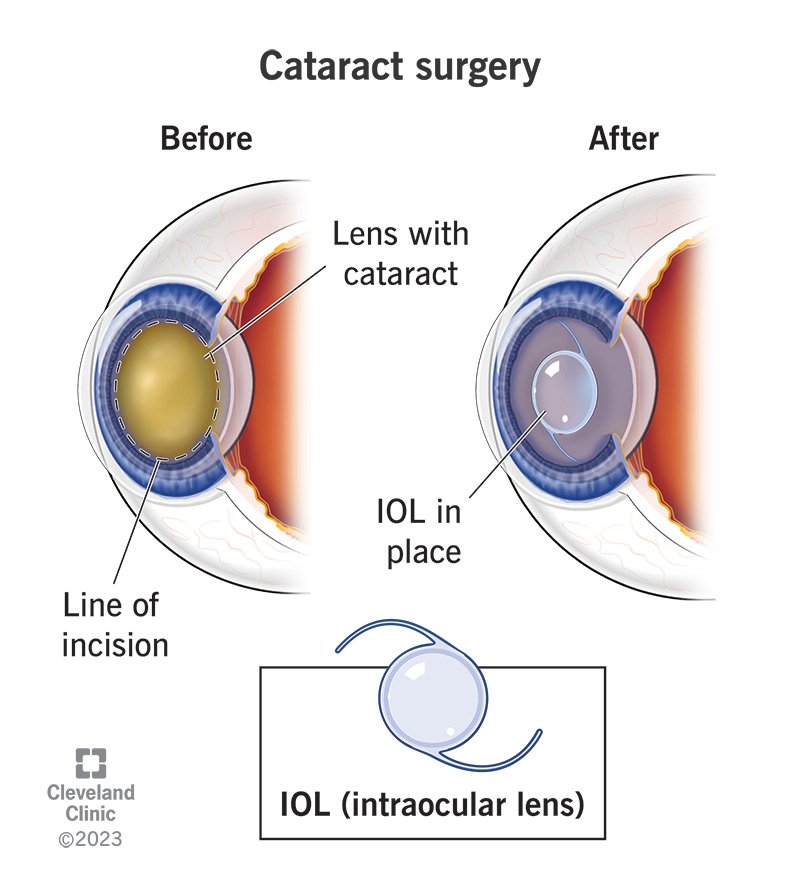
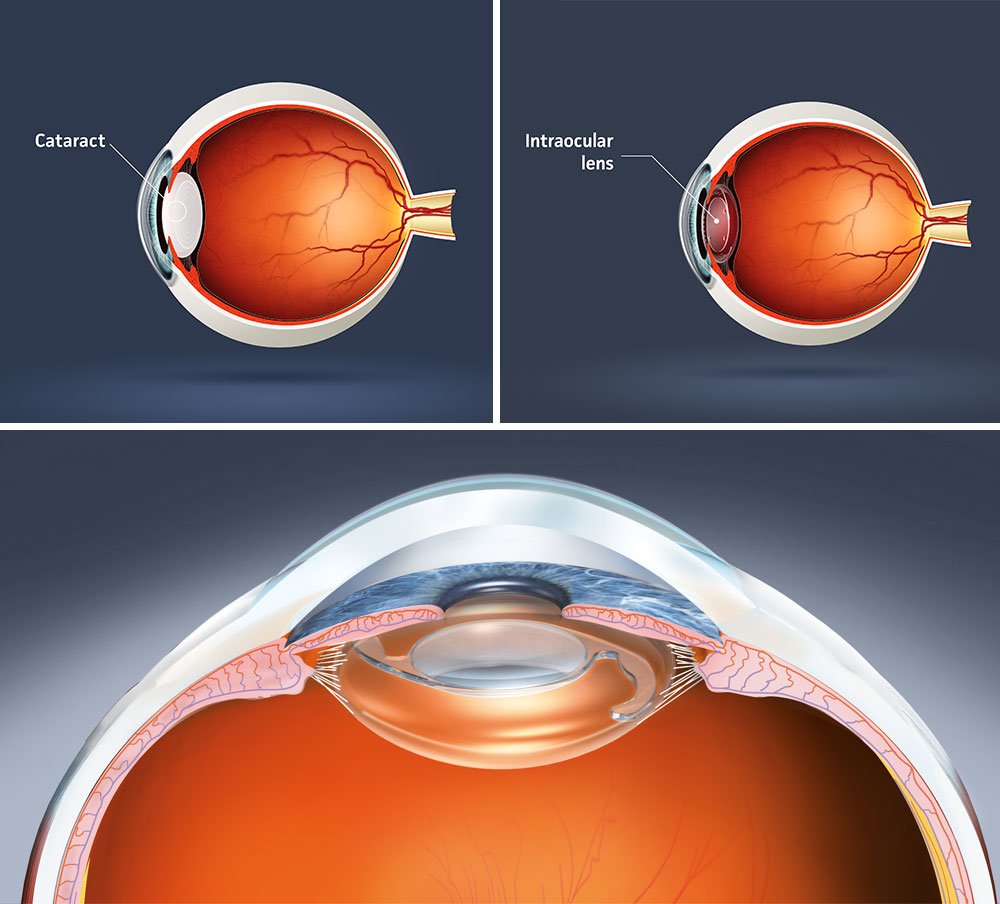
cataract is the clouding of the natural lens of the eye, which leads to blurred or diminished vision. It occurs due to the aging process, trauma, or other medical conditions, and it can significantly affect the quality of life.
The goal of
cataract surgery is to restore clear vision by removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens, called the
intraocular lens (IOL).
2. Types of Cataract Surgery Performed
At an advanced hospital like
Deep Netralaya, the following types of cataract surgery may be performed based on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s expertise:
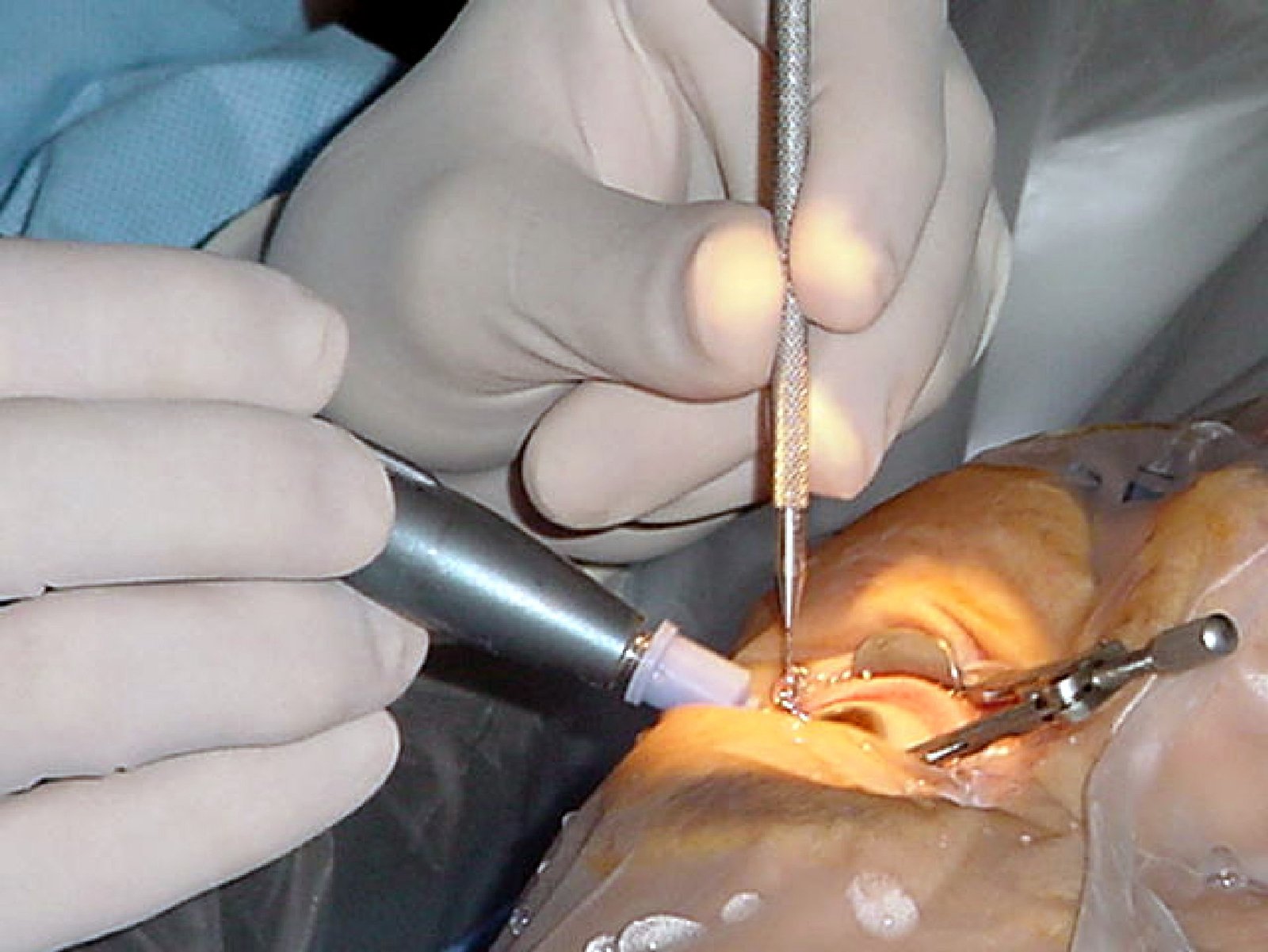
a) Phacoemulsification (Small Incision Cataract Surgery):
- Phacoemulsification is the most common and advanced method of cataract surgery performed today.
- It involves the use of high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to break up the cataract into tiny fragments, which are then gently suctioned out of the eye.
- A small incision is made (typically 2-3 mm), and the surgery is minimally invasive, leading to quicker recovery times.
- The patient’s cloudy lens is replaced with an intraocular lens (IOL), which is implanted through the same small incision.
- This procedure is usually done under local anesthesia and can be completed in less than 30 minutes.
b) Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery (FLACS):
- FLACS is a more advanced, precise form of cataract surgery. It uses a femtosecond laser to create incisions and soften the cataract, which can lead to a more controlled and effective removal.
- The femtosecond laser also helps in creating a precise opening in the capsule that holds the lens, which improves accuracy and reduces the need for manual surgical steps.
- This technique can be particularly beneficial for patients with dense cataracts, astigmatism, or those requiring highly accurate surgical procedures.
c) Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery:
- This technique is used in certain cases, where phacoemulsification is not appropriate.
- A small incision is made, and the cataract is removed manually. The IOL is then placed into the eye.
- This method is often employed in cases of complex cataracts or for patients who may not be ideal candidates for laser-assisted or phacoemulsification surgeries.
3. Preoperative Assessments
Before performing cataract surgery, several important steps are taken to ensure the best surgical outcome:
- Comprehensive Eye Exam: The patient undergoes a complete eye examination to assess the overall health of the eye, the type of cataract, and any other potential eye conditions (e.g., glaucoma or retinal issues).
- IOL Measurement: The size and shape of the eye are measured to determine the most suitable intraocular lens (IOL). This ensures the lens will provide optimal vision correction post-surgery.
- Patient Counseling: The surgeon discusses the available options for IOLs (monofocal, multifocal, toric lenses, etc.) to ensure that the patient’s needs are met (e.g., for near, distance, or astigmatic vision correction).
4. Surgical Procedure
During cataract surgery at
Deep Netralaya, the following steps are typically followed:
- Anesthesia: The patient is given local anesthesia (eye drops or an injection near the eye) to numb the eye. Sedatives may also be used to help the patient relax.
- Incision: A small incision is made at the edge of the cornea to access the cataract.
- Cataract Removal: In phacoemulsification, ultrasound energy is used to break the cataract into small pieces, which are then suctioned out of the eye. In FLACS, a femtosecond laser is used for greater precision.
- IOL Implantation: Once the cataract is removed, the surgeon inserts an intraocular lens (IOL) into the eye to replace the natural lens. The IOL is folded and inserted through the incision, then unfolded inside the eye.
- Closure: The incision is typically self-healing, requiring no stitches. In some cases, small stitches may be used.
5. Intraocular Lenses (IOLs)
There are several types of IOLs available, depending on the patient’s needs:
- Monofocal IOL: Corrects for distance vision. Patients will likely need reading glasses for near tasks.
- Multifocal IOL: Provides multiple focal points (near, intermediate, and distance), reducing the need for glasses.
- Toric IOL: Designed for patients with astigmatism, correcting both cataracts and astigmatism simultaneously.
- Accommodating IOL: Allows the lens to shift position, improving near and distance vision.
The choice of IOL is customized based on the patient’s lifestyle needs, such as the desire for glasses-free vision at different distances.
6. Postoperative Care and Recovery
After cataract surgery at
Deep Netralaya, patients are carefully monitored during the recovery process:
- Immediate Recovery: Most patients are able to go home the same day after the surgery. Some mild discomfort or dryness in the eye is common initially.
- Postoperative Medications: Patients are usually prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Follow-up visits are scheduled to monitor healing, check for any complications, and adjust the prescription for glasses if necessary.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and swimming for a few weeks to allow the eye to heal.
7. Benefits of Cataract Surgery at Deep Netralaya
- Advanced Technology: Deep Netralaya uses the latest surgical techniques, such as femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery and phacoemulsification, ensuring precision and faster recovery.
- Experienced Surgeons: The hospital likely has skilled and experienced surgeons who specialize in cataract surgery and use advanced diagnostic tools to plan and execute the procedure.
- Comprehensive Care: From preoperative counseling to postoperative follow-up, Deep Netralaya provides comprehensive care to ensure a successful outcome.
- Customized IOL Options: With various types of intraocular lenses available, patients at Deep Netralaya can choose the best IOL option based on their visual needs and lifestyle preferences.
8. Complications (Rare but Possible)
Like all surgeries, cataract surgery carries some risk of complications, although they are rare:
- Infection: Postoperative infections can be prevented with proper care and medications.
- Inflammation: Some swelling or discomfort can occur but is usually manageable with anti-inflammatory drops.
- IOL Misalignment: In rare cases, the intraocular lens may shift from its correct position, requiring adjustment.
- Posterior Capsule Opacification (PCO): This is a condition where the posterior part of the lens capsule becomes cloudy after surgery, but it can be easily treated with a procedure called YAG laser capsulotomy.
Conclusion
At
Deep Netralaya, cataract surgery is a highly advanced, safe, and effective procedure aimed at restoring vision. By employing modern techniques such as
phacoemulsification,
femtosecond laser-assisted surgery, and offering a range of
intraocular lenses (IOLs), the hospital ensures that patients achieve optimal vision outcomes. The skilled surgeons, along with state-of-the-art technology and a comprehensive care approach, make cataract surgery at Deep Netralaya a reliable option for patients seeking to regain their vision and improve their quality of life.