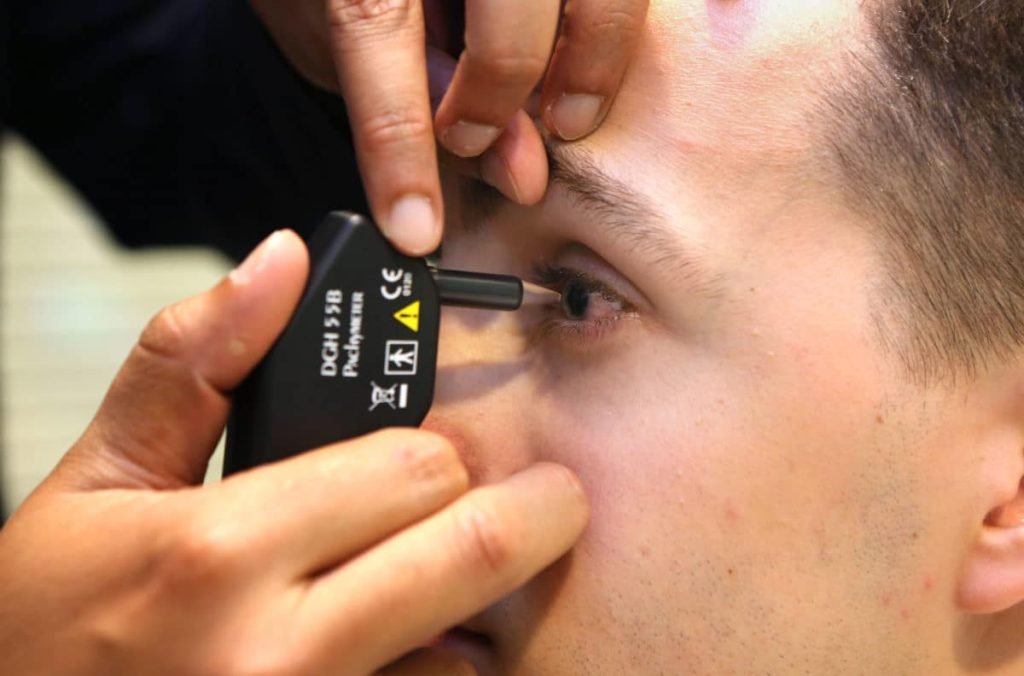
At Deep Netralaya, we offer the latest in diagnostic technology to ensure the highest level of accuracy in assessing and treating eye conditions. One such advanced diagnostic tool we use is the A-Scan (also known as an A-Scan Ultrasound), which is an essential test for evaluating the health of your eyes and determining the proper treatment
Why Choose Deep Netralaya for Your A-Scan?
- State-of-the-art Technology: We use the latest, high-quality A-scan machines to ensure the most accurate readings.
- Expert Care: Our skilled team of ophthalmologists and technicians are trained in using this technology to provide you with the best care possible.
- Patient Comfort: We prioritize your comfort and make sure the procedure is done smoothly and efficiently, with no discomfort or downtime.